Thermal Power Plant
1. Overview of Thermal Power Industry
The thermal power industry is a crucial sector within the energy industry, involving the conversion of fuels (often coal, oil, natural gas, or renewable energy sources) into electricity. This process typically entails burning fuel to generate heat, using that heat to turn water into steam, and then utilizing the steam to rotate turbine and generate electricity. The thermal power sector plays a significant role in supplying energy for the global economy.

Duyen Hai 2 Thermal Power Plant 2 (source: Internet)
2. Applications of Boilers in the Thermal Power Industry
In a thermal power plant, boilers are devices that absorb the heat generated during the combustion of various fuels to produce steam, which serves as the working fluid in the heat cycle, rotating steam turbines and generators to generate electricity. Boilers are the most important, largest and complex equipment directly influencing the operational efficiency, capital investment and safety aspects of the entire thermal power plant.
There are various methods of classifying boilers in thermal power plants, one of which is based on their function. According to this method, there are two main types: main boilers and auxiliary boilers.
a. Main boiler
The main boiler is typically a steam boiler responsible for efficiently and rapidly producing steam from water. This steam is then utilized to rotate turbines, generating electrical power.
Main boilers in thermal power plants are usually designed to meet the energy requirements of the entire system. Typically, the pressure can reach hundreds of bar.g and the temperature can exceed 500°C—much higher than saturated steam boilers in industrial applications. The choice of the main boiler type depends on the specific power requirements, stability and business environment of the particular thermal power plant.
For instance, circulating fluidized bed boilers or pulverized coal-fired boilers are often used in coal-fired thermal power plants due to their high capacity, meeting the load demands of the power unit. In combined cycle gas turbine power plants, the exhaust gas from the gas turbine passes through a heat recovery boiler to harness the excess heat, generating steam to rotate a steam turbine connected to a power generator.
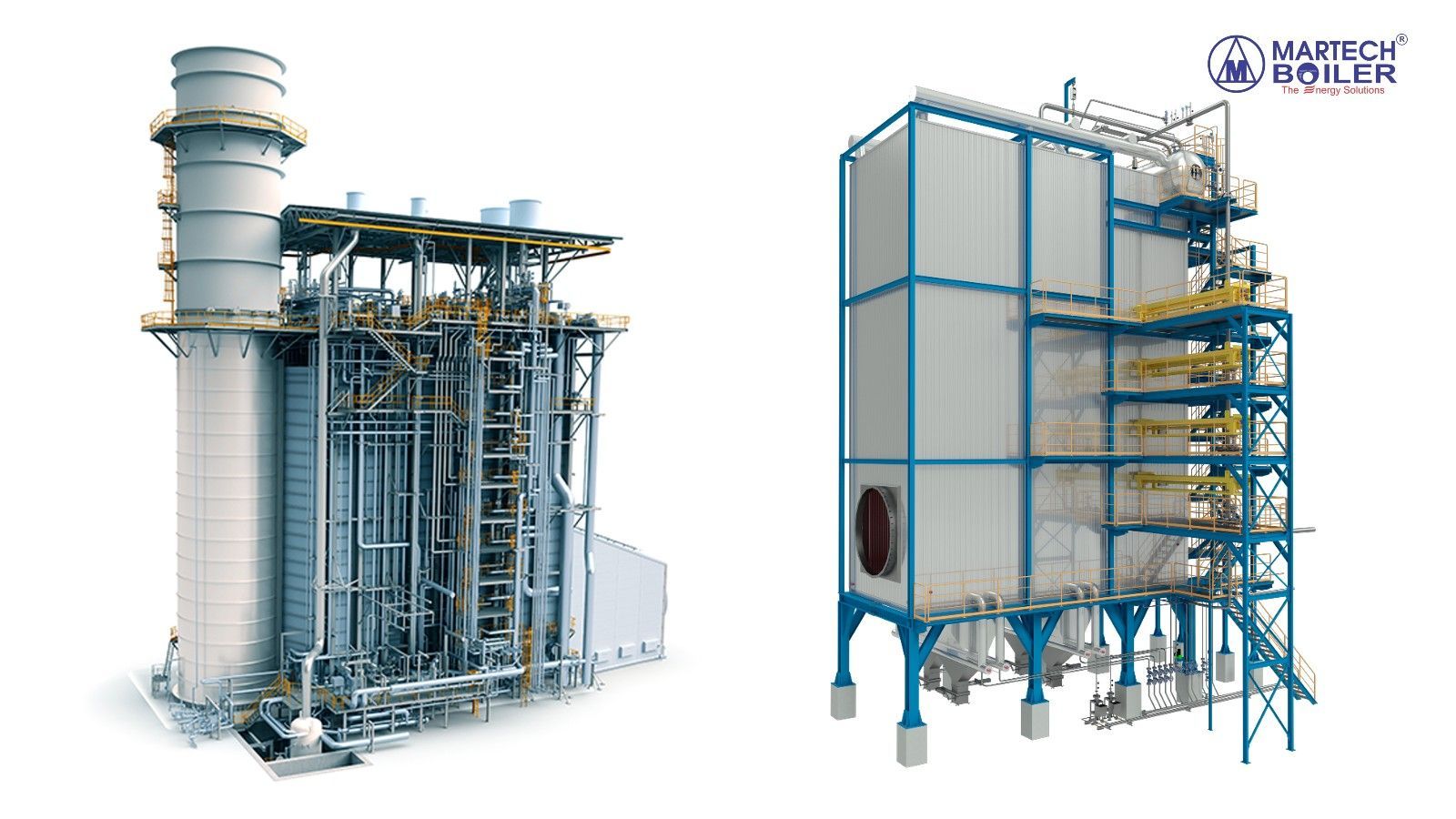
Recovery Heat Boilers in Gas Power Plant (left) and Waste-to-Energy Power Plant (right)
To ensure performance, safety, and compliance with environmental regulations, the main boilers in a thermal power plant typically need to meet various specific requirements and criteria, including:
- High Efficiency: The boiler must have high thermal conversion efficiency to optimize steam production from the fuel.
- Safety and Environmental Compliance: It must comply with labor safety regulations and environmental standards to ensure the safety of personnel and minimize negative impacts on the environment.
- Load Flexibility: The boiler needs to be able to withstand varying loads and be flexible to cope with fluctuations in energy demand.
- Fuel Savings and Energy Efficiency: It should be designed to save fuel and optimize energy efficiency.
- Ease of Maintenance and Repair: A design that facilitates maintenance and repairs is essential to reduce downtime and maintenance costs.
- Emission Control: Measures to control emissions are necessary to minimize the impact on air quality and comply with environmental standards.
- Adherence to Industry Standards: The boiler must adhere to industry standards and regulations, such as the ASME Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code.
b. Auxiliary Boiler
Auxiliary Boiler serves the primary purpose of establishing safe and stable conditions for the operation of the main boiler in a thermal power plant. Specific functions of the start-up boiler include:
- Initiating the main boiler system and preparing for the steam production process.
- Conducting safety checks to ensure that all equipment and systems operate correctly and safely before putting the main boiler into operation.
- Providing the necessary temperature and pressure to ensure that the main boiler can start without issues.
- Purging trapped air from the system to ensure the stable performance of the main boiler.
- Testing the quality of the steam to ensure that the produced water meets specified standards and requirements.
Boilers utilizing oil or gas combustion technologies are often preferred as start-up boilers due to their compact size, rapid steam generation, simple operation, and intermittent operation, which helps minimize fuel operating costs.
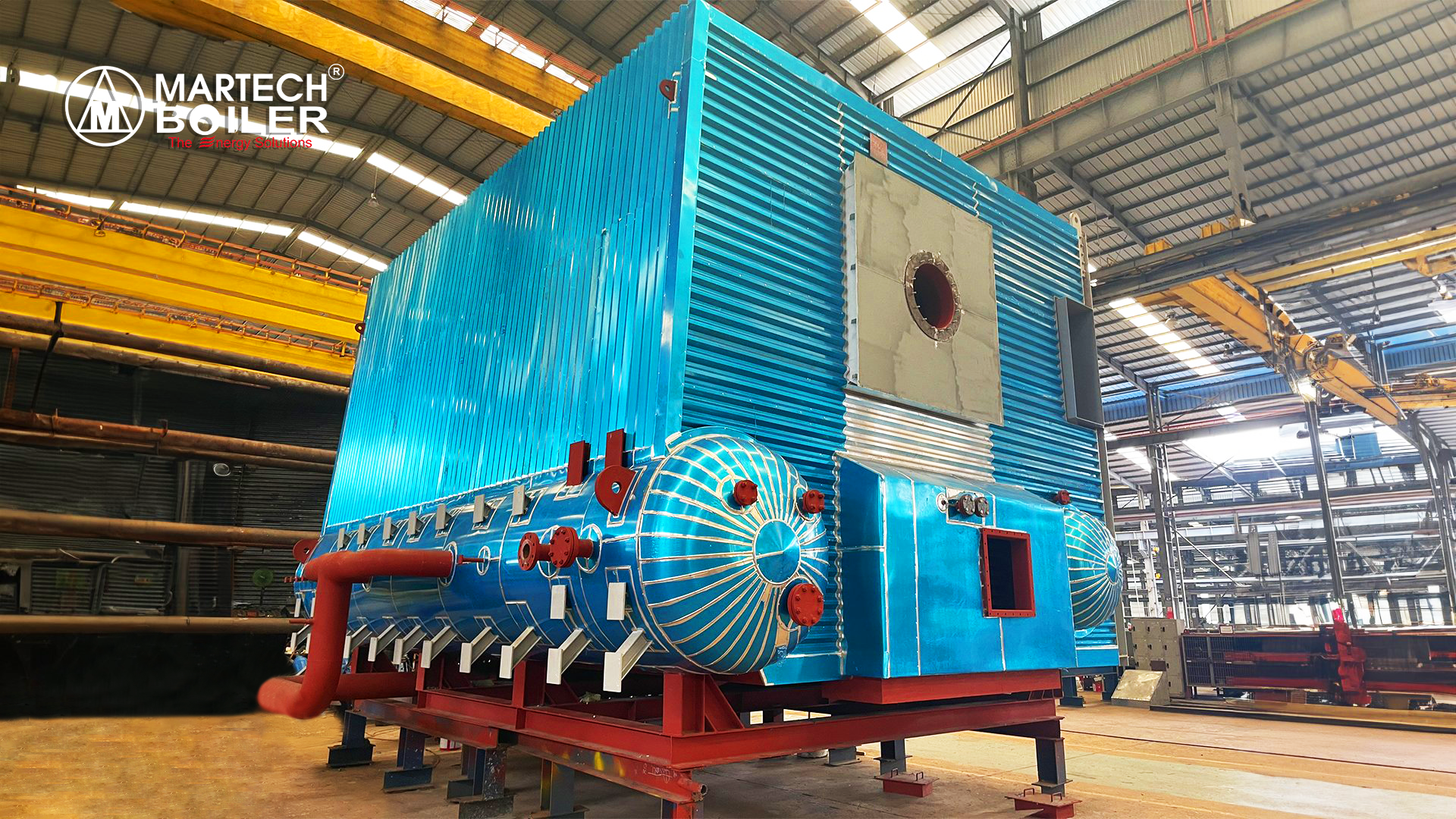

The auxiliary boiler burning Diesel, manufactured by Martech for the thermal power plant in the Northern region
Similar to the main boiler, the start-up boiler must also meet several crucial requirements, such as:
- Adherence to standards for occupational safety to protect employees during operation and maintenance.
- Ensuring that the start-up process does not have negative impacts on the environment and adhering to local and national environmental regulations.
- Producing high-quality steam and complying with the quality standards set for steam production.
- Being ease of maintenance and repair, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Having the ability to bear loads and flexibility to meet fluctuations in energy demand and system start-up capabilities.
- Optimizing energy efficiency to reduce fuel consumption and associated costs.
- Featuring a modern electronic control system to monitor and control start-up parameters, ensuring the process runs correctly and safely.
These requirements ensure that the auxiliary boiler not only performs its start-up function but also meets high standards of safety, efficiency, and maintenance, facilitating the continuous and efficient operation of the thermal power plant.
3. Martech's Projects
Martech provides various types of boilers and leads in technology advancements suitable for multiple industries, including the thermal power sector. With completed and ongoing projects, Martech becomes a reliable partner for many domestic thermal power plants.

