Textile & Garment
1.Overview of textile and garment industry
The textile industry is predominantly involved in the design, production, and distribution of fibers, fabrics, and garments. It stands as a major manufacturing sector, playing a vital role in the global economy. Beyond satisfying fundamental demands for clothing and textile goods, this industry makes substantial contributions to international trade and exports.
In Vietnam, the textile and garment industry stands out as one of the leading export sectors, experiencing rapid growth. In 2023, the export value of this industry reached a milestone of $40.3 billion, with a target set at $44 billion in 2024 (a 9.2% increase compared to the previous year). The swift expansion of the textile industry has provided significant impetus to Vietnam's economic growth, contributing to the improvement of income and living standards for many laborers.

The textile industry stands as one of the pivotal manufacturing sectors in Vietnam
Alongside opportunities, the rapid growth of the textile and garment industry also poses challenges related to energy demand and emission reduction. Therefore, to meet export expectations and sustain sustainability, the textile industry needs to focus on optimizing energy use and exploring energy-saving solutions to mitigate negative environmental impacts.
2. Applications of boilers in textile and garment industry
In a textile factory, the production process typically commences with the preparation and cleaning of fibers (whether synthetic or natural). Subsequently, these fibers are woven into fabric, and finally, garments or other textile products are manufactured.
Here's a overview of the manufacturing process in a textile plant:
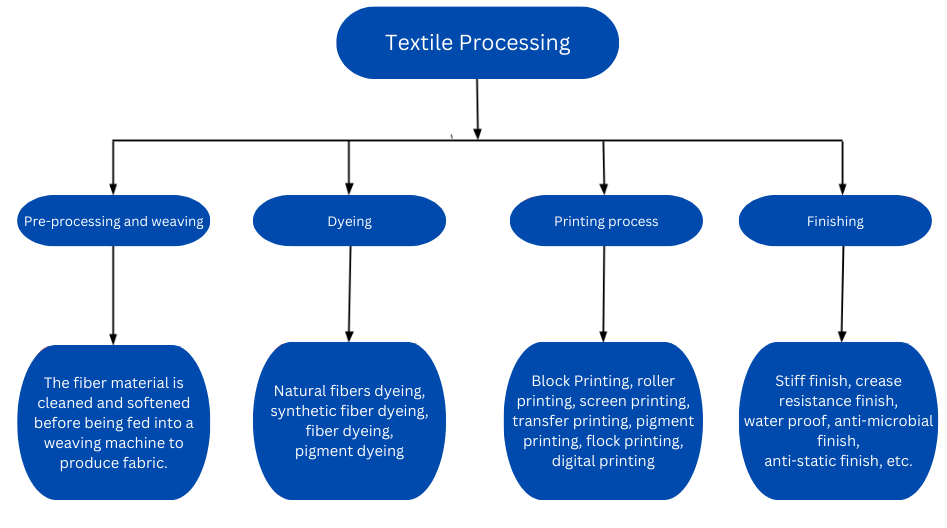
Every process involves the participation of steam or hot water, making boilers an indispensable equipment in textile factories:
- Pre-Treatment: This is a crucial step in the fabric processing procedure. Boilers play a role in supplying pure steam and hot water to eliminate dirt, oil, and other contaminants from the fabric fibers.
- Dyeing: This step involves adding color to the fabric and is crucial in determining the product's color. Steam is used to melt the dye bath, facilitating easy penetration of the dye into the fabric fibers, ensuring color durability and uniformity.
- Printing: This process enhances the aesthetic appeal of the product by adding designs to the fabric. Like dyeing, the printing process employs various methods depending on the fabric type and the desired final product. However, in this process, steam is used to heat the printing ink, helping it adhere to the fabric.
- Finishing: Boilers are employed to heat the fabric in the finishing process, eliminating wrinkles and creating a smooth surface for the final product.
Due to the temperature stability requirements, thermal oil heaters have become a widely used energy solution in the textile industry. The automatic control capability of thermal oil heater helps maintain the desired temperature, enhancing the quality and uniformity of the final products. Additionally, thermal oil heaters offer flexibility in adjustment, responding quickly to fluctuations in the process, thereby reducing waiting times and optimizing the production process.
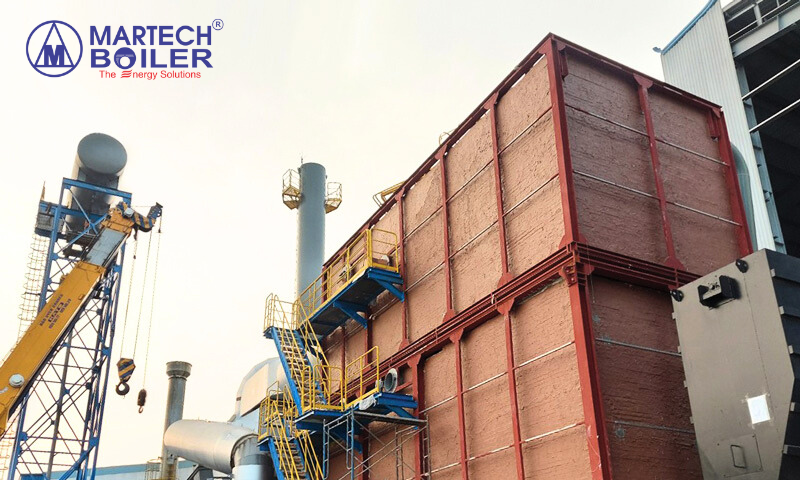

The 20 Gcal/h thermal oil heater that Martech installed for Dae Young Textile Factory (Dong Nai)
Alongside thermal oil heaters, biomass boilers are garnering attention due to the trend of transitioning to clean energy for environmental protection. Utilizing organic fuels such as wood, straw, sugarcane bagasse, etc., biomass boilers offer a renewable energy solution, enabling businesses to develop sustainably and reduce negative environmental impact.
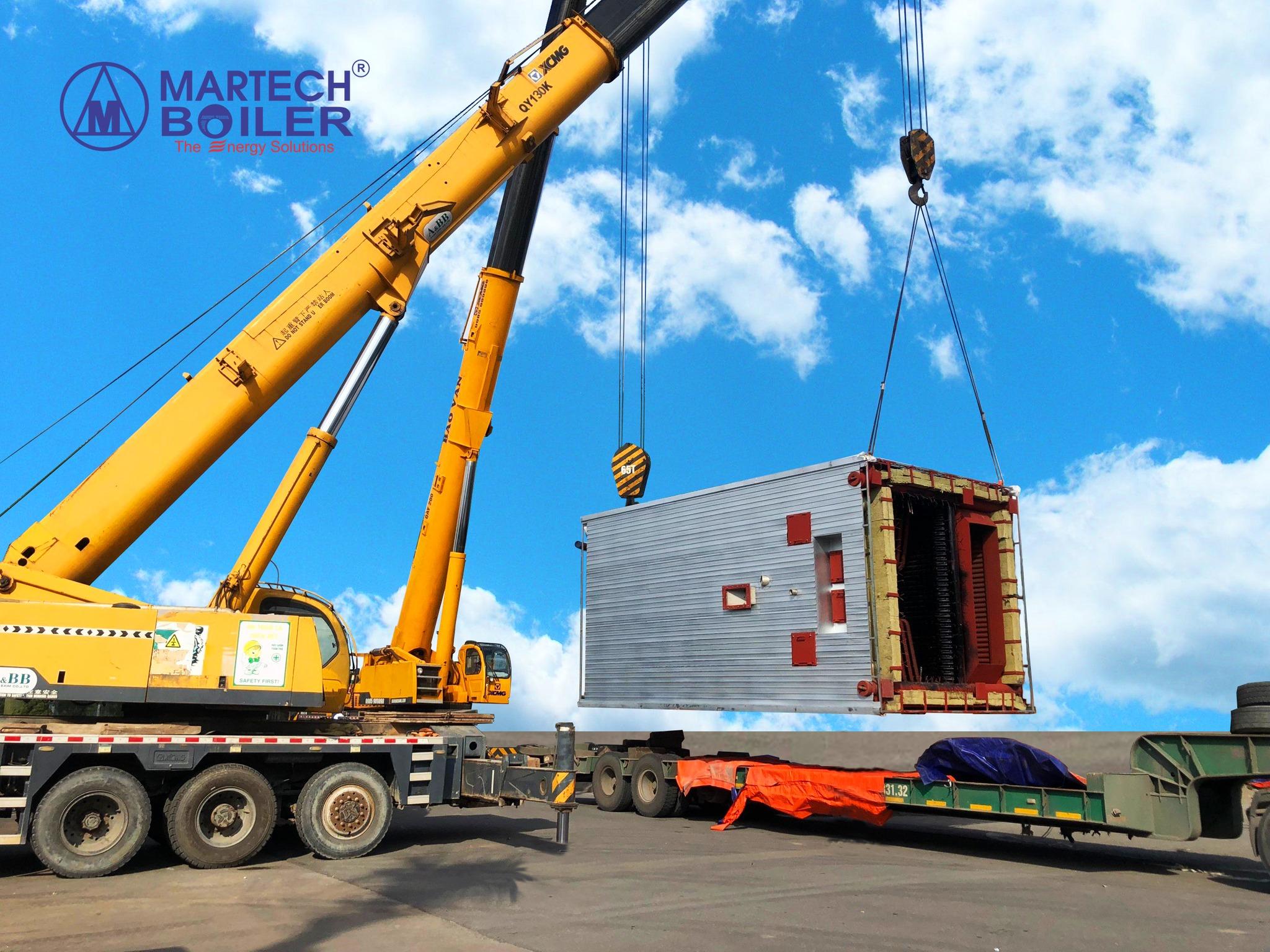

The 10TPH biomass boiler installed by Martech for a textile factory in Nam Dinh helps reduce 25,000 tons of CO2 emissions annually
3. Martech's projects


